235ML INJECTABLE VINYLESTER CHEMICAL ANCHOR

X2000 235ML
Low VOC injectable adhesive anchors
235ml vinylester injectable adhesive is a high performance and rapid curing two-part chemical anchoring system. With high loads capacity and chemical resistant.
A two-component 10:1 resin chemical anchoring injection system. Convenient setting and fast curing in low temperature. It is environmentally friendly item without styrene. All of our products had tested and approved in Germany according to EAD 330499-00-0601. There are also 150ml, 345ml, 360ml and 380ml for diverse market preference.
Chemical fixing system – Fast curing viny lester chemical anchor
The obvious characteristic of vinylester hybrid mortar is fast curing to save installation time and hardening time. We develop diverse curing time to meet different country weather and installation temperature. Fast curing formula is not suitable for nonstandard high temperature which caused curing time accelerated. Please check technical data sheet for safety installation.
Specification of X2000 vinylester chemical anchor
- Material: Vinylester Styrene Free
- Model Number: X2000
- Size: 235ml
- Shelf Life: 18 months
- Mixing Ratio: 10:1
- Mixed Color: Gray
- Standard Package: One cartridge with one mixer
- Other Accessory: Mixer, caulking gun, nylon sleeve, air pump, brush
Vinylester chemical anchor is has excellent chemical resistance
- High load performance and increase productivity
- Rapid curing time
- Styrene free and low VOC
- Great resistance to corrosion
- Fit to standard caulk guns
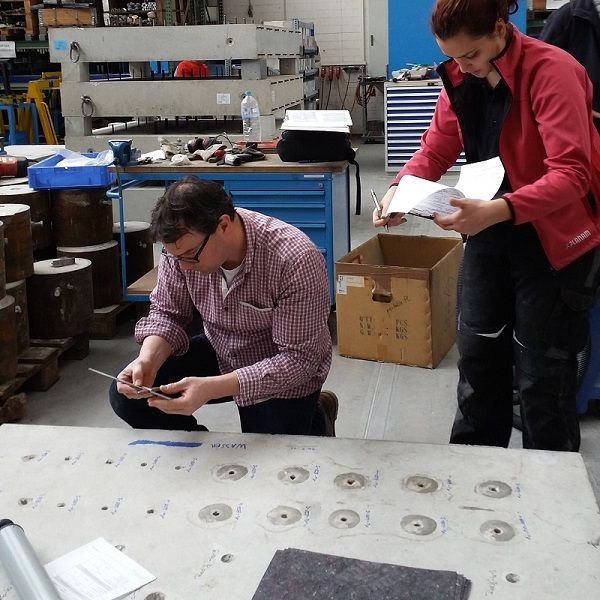
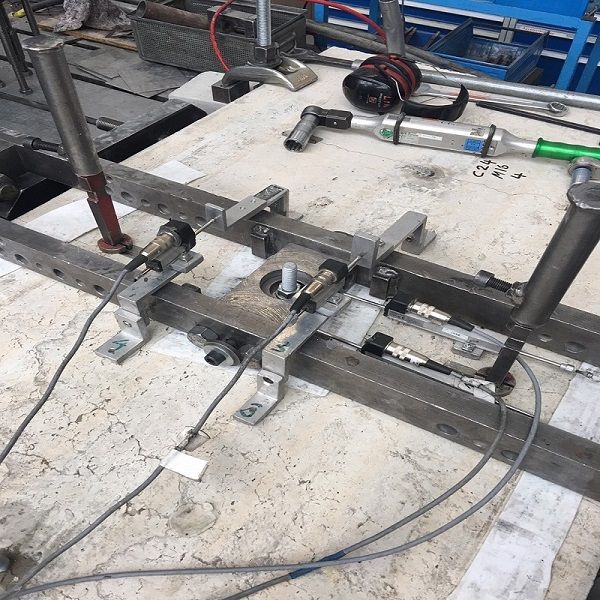


Vinylester glue anchor suitable for wall and overhead applications
The rapid curing vinylester glue anchor is perfect for wall and overhead applications. It is suitable for fixing studs for air conditional support bracket, shopping mall signs, lamps, and fire sprinkler system. With the heavy load capacity, 235ml vinylester chemical anchor provides high performance in solid elements, concrete, granite, and stone.


Technical Data
CHART 1. SOLID SUBSTRATE REBAR INSTALLATION DETAILS
| Pressure | Destroy Haul Strength (Kgf/KN) |
Safety Haul Strength (Kgf/KN) |
Working Standard (mm) |
||||||
| Concrete Strength | 4,000 psi | 280 kg/cm2 | 4,000 psi | 280 kg/cm2 | Hole Diameter | Hole Depth | |||
| Rebar No. | #3 | (Φ10) | 3,540 | 35.8 | 1,180 | 11.9 | 13 | 90 | |
| #4 | (Φ13) | 5,490 | 55.4 | 1,827 | 18.5 | 16 | 120 | ||
| #5 | (Φ16) | 9,060 | 91.5 | 3,020 | 30.5 | 20 | 145 | ||
| #6 | (Φ19) | 14,150 | 142.9 | 4,717 | 47.6 | 25 | 170 | ||
| #7 | (Φ22) | 18,630 | 188.2 | 6,210 | 62.7 | 28 | 200 | ||
| #8 | (Φ25) | 23,195 | 234.3 | 7,732 | 78.1 | 32 | 225 | ||
| #9 | (Φ29) | 25,340 | 256.0 | 8,447 | 85.3 | 37 | 250 | ||
| #10 | (Φ32) | 32,120 | 324.4 | 10,707 | 108.1 | 40 | 290 | ||
| Remarks: | 1. Concrete Strength fc’: 280kg/cm2 (4,000 psi) 2. Rebar Strength: #3~#5 fy: 2,800 kgf/cm2, #6~#11 fy= 4,200 kgf/cm2 |
||||||||
CHART 2. CURING TIME TABLE
| Temperature (°C) | Gelling | Full Curing |
| 5 | 90 min. | 8 hr. |
| 10 | 40 min. | 4 hr. |
| 20 | 18 min. | 1.5 hr. |
| 30 | 9 min. | 1 hr. |
| 40 | 6 min. | 1 hr. |
| Please make pull out test over 24 hours after full cured. | ||
CHART 3. FIXING CONSUMPTION PER CARTRIDGE
| Anchor Size | Hole Diameter (mm) |
Hole Depth (mm) |
Number of Fixings | ||||
| 235ml | 280ml | 345ml | 360ml | 380ml | |||
| M8 | 10 | 80 | 47 | 56 | 69 | 72 | 76 |
| M10 | 12 | 90 | 29 | 34 | 42 | 44 | 47 |
| M12 | 14 | 110 | 17 | 21 | 25 | 27 | 28 |
| M16 | 18 | 125 | 9 | 11 | 14 | 14 | 15 |
| M20 | 24 | 170 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| M24 | 28 | 210 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| M30 | 35 | 270 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| M36 | 40 | 330 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Note: Based on continuous installation without interruptions or nozzle changes. Provided as a guide and will vary with temperature. | |||||||
How to install chemical anchor?
1. Drill the specific hole size and depth. 2. Clean dust with brush and air blow pump. 3. Press out unmixed resin which can’t be used. 4. Inject mixed resin into drilled hole and fill from the bottom. 5. Insert rebar/threaded rod/steel strip. Curing time refer to TDS. Don’t touch until full curing. The installation process will affect the bonding performance of chemical anchors.

